Linear Regression: Gradient Descent
Linear Regression and Gradient Descent
Linear Regression & Gradient Descent is the first algorithm I came across When I decided to get into Data Science through Andrew Ng’s Machine Learning course and after that through my Master’s Program Every other algorithm I implemented since is based on these basic algorithms and it fascinates me every time. Lets dive into it:
Linear Regression:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("/path")
data.head(1)
data.shape
data.head()
Feature scaling for Multivariate Problem
Why is Feature Scaling Important
data =data.values
m=len(data[:,-1])
X=data[:,0:2].reshape(m,2)
mean=np.mean(X,axis=0)
std=np.std(X,axis=0)
X = (X - mean)/std
X = np.append(np.ones((m,1)),X,axis=1)
y=data[:,-1].reshape(m,1)
theta=np.zeros((3,1))
Closed-Form Equation Vs Gradient Descent Vs Stochastic Gradient Descent
Explain the differences between alternative approaches to estimating the parameters of a model
Closed-form formula or Normal Equation
We dont need to implement feature scaling in this case.
Formula:
XT=X.T
XTX=XT@X
inv=np.linalg.pinv(XTX)
thetanew=(inv@XT)@y
print(thetanew)
[[89597.90954361]
[ 139.21067402]
[-8738.01911255]]
Finding Cost Function or Loss Function for gradient descent
def computeCost(X,y,theta):
m=len(y)
err=((np.dot(X, theta)) - y)**2
jtheta = (np.sum(err) *( 1/ (2*m)))
return jtheta
computeCost(X,y,theta)
65591548106.45744
Gradient Descent
def gradientDescent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations):
m = len(y)
history = []
for i in range(iterations):
descent = alpha * 1 / m * (np.dot(X.transpose(), ((np.dot(X,theta)) - y)))
theta -= descent
history.append(computeCost(X, y, theta))
return theta, history
thetanew1,chistory1= gradientDescent(X,y,theta,1,50)
print(thetanew1)
[[340412.65957447]
[109447.79646961]
[ -6578.35485416]]
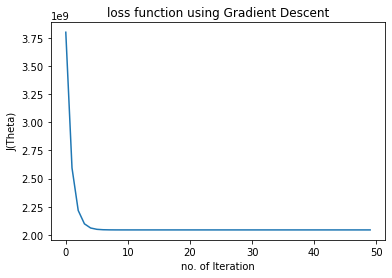
plt.plot(chistory1)
plt.xlabel("no. of Iteration")
plt.ylabel("J(Theta)")
plt.title("loss function using Gradient Descent")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'loss function using Gradient Descent')
Stochastic Gradient Descent
def stocashtic_gradient_descent(X, y, theta, alpha, iterations):
m = len(y)
cost_history = np.zeros(iterations)
for i in range(iterations):
cost = 1.0
for j in range(m):
rand_ind = np.random.randint(0, m)
Xi = X[rand_ind, :].reshape(1, X.shape[1])
yi = y[rand_ind].reshape(1, 1)
descent = (1 / m) * alpha * (Xi.transpose().dot(((np.dot(Xi, theta)) - yi)))
theta -= descent
cost += computeCost( Xi, yi, theta)
cost_history[i] = cost
return theta, cost_history
thetanew2,chistory2 = stocashtic_gradient_descent(X,y,theta,1,100)
print(thetanew2)
[[333857.22454677]
[104732.15569427]
[ -7188.6376759 ]]
n_iter = 100
theta = np.random.randn(3,1)
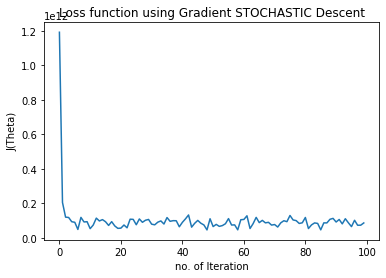
plt.plot(range(n_iter),chistory2)
plt.xlabel("no. of Iteration")
plt.ylabel("J(Theta)")
plt.title("Loss function using Gradient STOCHASTIC Descent")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Loss function using Gradient STOCHASTIC Descent')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33, random_state=42)
m = len(y_train)
computeCost(X_train,y_train,thetanew1)
1654614139.0828218
computeCost(X_test,y_test,thetanew1)
2796320254.1728415
computeCost(X_train,y_train,thetanew2)
1636964355.6928473
computeCost(X_test,y_test,thetanew2)
2833744177.3070307
thetap1,phistory1 = gradientDescent(X_train,y_train,theta,0.2,50)
print(thetap1)
[[319924.75939214]
[ 93648.11271015]
[ -2496.78859906]]
thetap2,phistory2 = stocashtic_gradient_descent(X_train,y_train,theta,0.2,90)
print(thetap2)
[[321087.62748613]
[ 91245.71339344]
[ -3415.62095041]]
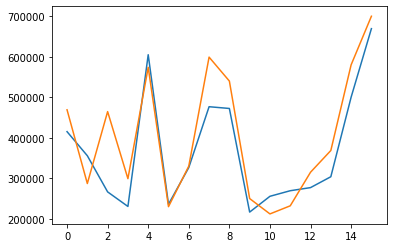
predictions1 = []
for i in range(0,16) :
predict1= np.dot(thetanew1.transpose(),X_test[i])
predictions1 = np.append(predictions1,predict1)
plt.plot(predictions1)
plt.plot(y_test)
predictions = []
for i in range(0,16) :
predict= np.dot(thetanew2.transpose(),X_test[i])
predictions = np.append(predictions,predict)
plt.plot(predictions)
plt.plot(y_test)
Prediction vs ground truth
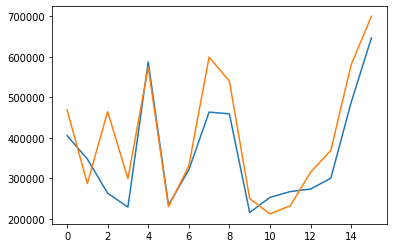
eval1,ehistory1 = gradientDescent(X_test,predictions1,theta,0.08,150)
print(thetap1)
eval2,ehistory2 = gradientDescent(X_test,y_test,theta,0.08,150)
predictions = []
for i in range(0,16) :
predict= np.dot(thetap2.transpose(),X_test[i])
predictions = np.append(predictions,predict)
print(predictions)
[381901.00005848 336311.78918155 253740.50903145 222780.39041256
545581.6271754 227460.40834332 305580.70764912 440592.18871572
436872.17446306 210780.34443624 244380.47316992 250609.53324454
262860.54397345 280369.6472658 455221.28097376 612323.81046984]
testtheta1,ethistory1 = gradientDescent(X_test,y_test,theta,0.1,400)
print(testtheta1)
[[376464.08973221]
[108344.58280849]
[ -1408.17517797]]
m1=len(predictions)
ypred=predictions.reshape(m1,1)
eval1,ehistory1 = gradientDescent(X_test,ypred,theta,0.08,150)
print(eval1)
[[318537.53041957]
[ 94344.63835206]
[ -1437.15342375]]
Gradient Descent with Regularization
m1=len(predictions)
ypred=predictions.reshape(m1,1)
eval1,ehistory1 = gradientDescent(X_test,ypred,theta,0.08,150)
print(eval1)
def computeCostR(X,y,theta,Lambda):
m=len(y)
predictions=X.dot(theta)
square_err=(predictions - y)**2
cost = 1/(2*m) * np.sum(square_err)
regcost = cost + Lambda/(2*m) * sum(theta**2)
j_0= 1/m * (X.transpose() @ (predictions - y))[0]
j_1 = 1/m * (X.transpose() @ (predictions - y))[1:] + (Lambda/m)* theta[1:]
grad= np.vstack((j_0[:,np.newaxis],j_1))
return regcost[0], grad
computeCostR(X,y,theta,0.1)
(2195587442.501597, array([[-1754.41032517],
[-2677.15865359],
[ 2644.26335941]]))
def gradientDescentR(X,y,theta,alpha,num_iters,Lambda):
m=len(y)
history =[]
for i in range(num_iters):
cost, grad = computeCostR(X,y,theta,Lambda)
theta = theta - (alpha * grad)
history.append(cost)
return theta , history
thetanew3 , chistory3 = gradientDescentR(X,y,theta,1,10,0.1)
print("The regularized theta using ridge regression:\n",thetanew3)
The regularized theta using ridge regression:
[[340412.65957447]
[108768.39338594]
[ -6362.50331981]]
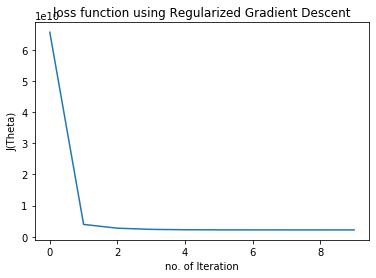
plt.plot(chistory3)
plt.xlabel("no. of Iteration")
plt.ylabel("J(Theta)")
plt.title("loss function using Regularized Gradient Descent")
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'loss function using Regularized Gradient Descent')